Could Smartphone Addiction Be Linked to Low Testosterone Levels in Men
Smartphones have become integral to our daily lives, offering convenience and connectivity like never before. However, the presence of these devices has raised concerns about the potential impact on various aspects of our well-being, including hormonal health. One area that has garnered significant attention is the possible link between smartphone addiction and low testosterone levels in men.
The use of smartphones, coupled with the rise of social media and addictive mobile applications, has led to a phenomenon known as “smartphone addiction.” This excessive and compulsive use of smartphones has been associated with various negative consequences, from sleep disturbances and depression to impaired social interactions and decreased productivity.
Does Screen Time Lower Testosterone?
Research suggests a potential link between prolonged screen time, particularly excessive smartphone usage, and reduced testosterone levels in men. A 2014 paper published in Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine investigated the effects of mobile phone radiation on testosterone in rats. The findings showed a significant decrease in testosterone levels in the exposed group compared to the control group.
While human studies are needed to confirm these findings, it raises a red flag, especially considering the detrimental effects of low testosterone in men. Reduced testosterone can lead to decreased muscle mass, bone density, libido, and cognitive function, highlighting the importance of this potential connection.
The Mechanisms Behind Smartphone Addiction
Smartphone addiction is a complex phenomenon driven by both psychological and neurological factors. The constant influx of notifications, social media interactions, and endless content creates a powerful reward system that activates the brain’s dopamine pathways, reinforcing addictive behaviour. In addition, smartphone screens’ blue light transfer can disturb the body’s natural circadian rhythms, potentially contributing to hormonal imbalances and increased oxidative stress, negatively impacting testosterone production.
Lifestyle Factors and Testosterone
While smartphone addiction may play a role in lowering testosterone levels, it is important to acknowledge other lifestyle factors that can influence hormone regulation. Sedentary behaviour, poor diet, lack of sleep and chronic stress can all contribute to decreased testosterone production. Engaging in physical activity, consuming a balanced diet packed with nutrients, and practising stress management can help maintain healthy testosterone levels. Oxidative stress has also been linked to low testosterone levels, highlighting the importance of a balanced lifestyle.
Potential Health Consequences of Low Testosterone
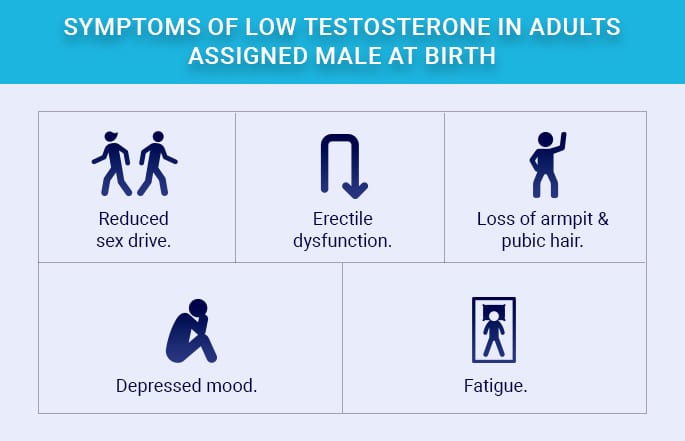
Low testosterone levels can have severe consequences on men’s health. Lessened sexual function, including low libido and erectile dysfunction, is a common concern. Additionally, low testosterone can contribute to muscle loss, decreased bone density, and a heightened risk of osteoporosis. Metabolic issues like insulin resistance and obesity are also potential consequences.
Cardiovascular health may suffer due to adverse effects on cholesterol and blood pressure levels. Emotional well-being can be affected, leading to fatigue, irritability, and depression. Addressing low testosterone is crucial to prevent these detrimental effects on physical and mental health.
The Sleep Connection: Does Scrolling Before Bed Matter?
Adequate sleep is important for optimal testosterone production, and disruptions to sleep patterns can have a negative impact on hormone synthesis. Using smartphones before bedtime can interfere with sleep quality and duration due to the blue light exposure and mentally stimulating content. This disruption can contribute to increased oxidative stress levels and impaired testosterone production, potentially exacerbating the effects of smartphone addiction on hormonal balance. Additionally, the absence of quality sleep can lead to fatigue, cognitive impairment, and other health issues, further heightening the potential consequences of low testosterone levels. Reducing exposure to blue light can be achieved by altering phone settings or adding an app that blocks the blue light and gives off an orange hue. Alternatively, blue light blocking glasses can be worn.
More Than Testosterone: Wider Health Implications
While the potential link between smartphone addiction and low testosterone is concerning, the implications of excessive smartphone use extend beyond hormonal imbalances. Research has suggested associations with mental health issues like anxiety, depression, and decreased self-esteem.
Excessive smartphone use can result in oxidative and chronic stress, which can have far-reaching negative impacts on overall well-being. This further highlights the importance of developing healthy technology habits.
Taking Charge of Your Hormonal Health
The potential connection between excessive smartphone usage and low testosterone levels in men is an emerging area of concern that needs further investigation. While existing research highlights a possible link, more comprehensive studies are required to entirely understand the mechanisms and extent of this relationship.
Nonetheless, the potential implications of hormonal imbalances on various aspects of health underscore the importance of raising awareness about the risks of smartphone addiction. Individuals, healthcare professionals, and researchers should prioritise promoting balanced technology usage and overall well-being to mitigate any potential negative impacts on hormonal health and beyond.
To understand the symptoms of low testosterone or hormonal imbalances, Helvetica Healthcare offers comprehensive testing and treatment solutions. We aim to provide efficient testing and diagnostic products that enhance lab research capabilities to detect OS biomarkers. Our range of OXIDATIVE STRESS assay kits and standards is designed to assist in exploring oxidative stress markers and metabolites in human & animal samples as well as samples exposed to drugs and foods.
The TBARS (Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances) assay has become the assay of choice for screening and monitoring lipid peroxidation, a primary indicator of oxidative stress. The assay can be used with many types of samples, including drugs, food products, and material of human and animal origin, and it provides standardised and reproducible results.
Visit the Helvetica Health Care website to purchase our products.